Omega-3 fatty acids are among the most popular supplements on the market today, thanks to their impressive range of health benefits—from heart support to brain function. The most common sources of these essential fats are fish oil and the lesser-known harp seal oil. While both deliver EPA and DHA, not all omega-3s are created equal.
Let’s break down the key differences between fish oil and harp seal oil, so you can decide which one best suits your lifestyle and health goals.
1. What Are They Made From?
- Fish Oil is extracted from the tissue of oily fish like sardines, mackerel, anchovies, and salmon.
- Harp Seal Oil is derived from the blubber of harp seals, marine mammals native to the Arctic and North Atlantic.
Both sources provide rich amounts of omega-3 fatty acids, but their composition and bioavailability can differ.
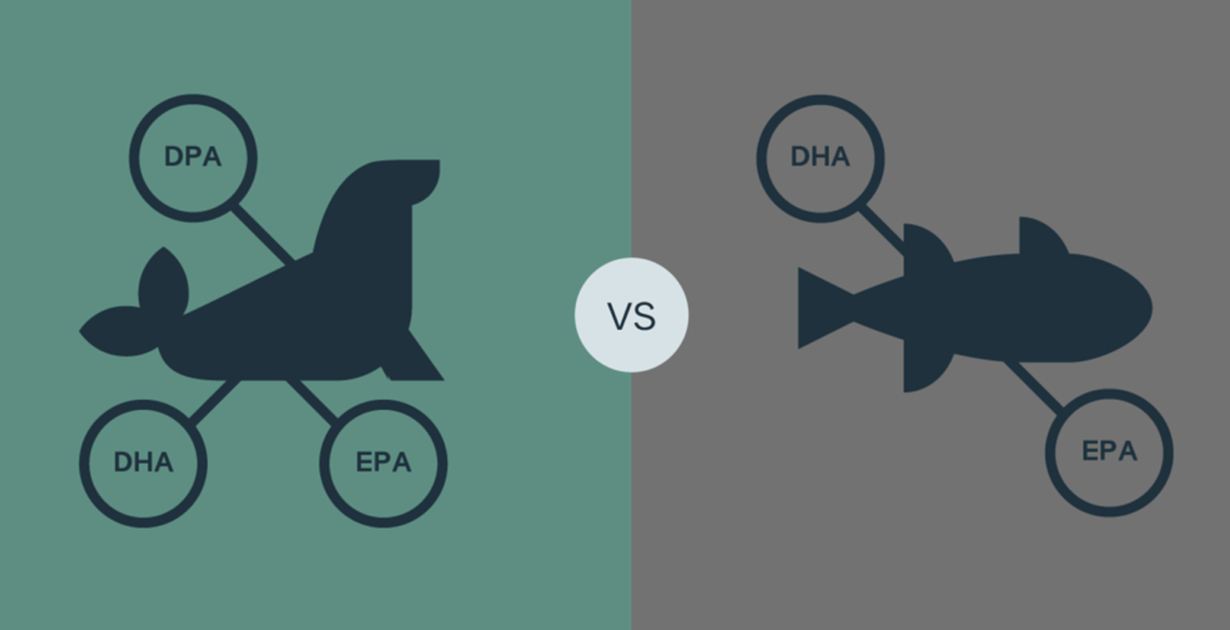
2. Omega-3 Content: EPA, DHA, and DPA
- Fish Oil primarily contains two key omega-3s:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
- Harp Seal Oil contains:
- EPA
- DHA
- DPA (Docosapentaenoic Acid) – A less common but highly beneficial omega-3 not typically found in fish oil.
DPA is believed to enhance the benefits of EPA and DHA, possibly improving cardiovascular health and reducing inflammation more effectively. This gives harp seal oil a unique edge, especially for people looking for a more complete omega-3 profile.
3. Absorption and Bioavailability
Seal oil omega-3s are naturally in the triglyceride form, which may be more easily absorbed by the human body compared to some processed fish oils, which often come in ethyl ester form. Though high-quality fish oils can also be found in triglyceride form, seal oil is more often naturally bioavailable.
4. Taste, Smell, and Digestion
- Fish oil is notorious for causing fishy aftertaste or “fish burps” in some users.
- Seal oil tends to be more neutral in taste and smell, and many people find it gentler on digestion.
5. Sustainability and Ethics
This is where the comparison becomes more complex:
- Fish Oil is widely accepted and produced, though overfishing and unsustainable practices can be a concern with some brands. Choosing sustainably sourced fish oil is important.
- Harp Seal Oil is more controversial due to the ethical debates around seal hunting. While Indigenous and regulated harvesting practices are often sustainable and humane, commercial seal hunting has been criticized by animal rights groups. Seal oil is banned in some regions, including the European Union (with exemptions for Indigenous use).
If ethical sourcing is a top concern for you, be sure to research the origins and certifications of any seal oil product.
6. Availability and Regulation
- Fish Oil is widely available globally in multiple forms: capsules, liquids, gummies, and more.
- Seal Oil is less common and not available in every country due to legal restrictions. It’s often found in Canada, some Arctic nations, and among Indigenous communities.
7. Cost Comparison
- Fish Oil is generally less expensive and more accessible due to its mass production.
- Seal Oil tends to be more costly and niche, partly due to limited availability and specialized sourcing.
Bottom Line
If you’re looking for a widely available, affordable source of EPA and DHA, fish oil is a reliable and well-researched choice—especially if you choose a high-quality, sustainably sourced brand.
If you want the added benefits of DPA, prefer gentler digestion, or are looking for a more complete omega-3 profile, harp seal oil may be worth considering—provided it’s available in your region and ethically sourced.
Whichever you choose, be sure to consult your doctor before starting any supplement, especially if you’re pregnant, nursing, or taking medication.



Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *